Cortisol Stimulates Gluconeogenesis Through Which of the Following Mechanisms
Increasing levels of PEPCK phosphoenol carboxykinase Decreasing levels of fructose 2 6 biaphosphate Activating phoephofructokinaso-1 Phosphorylating hormone sensitive lipase. Cortisol restores homeostatic mechanisms after the body is exposed to stress.
Ijms Free Full Text The Jekyll And Hyde Of Gluconeogenesis Early Life Adversity Later Life Stress And Metabolic Disturbances Html
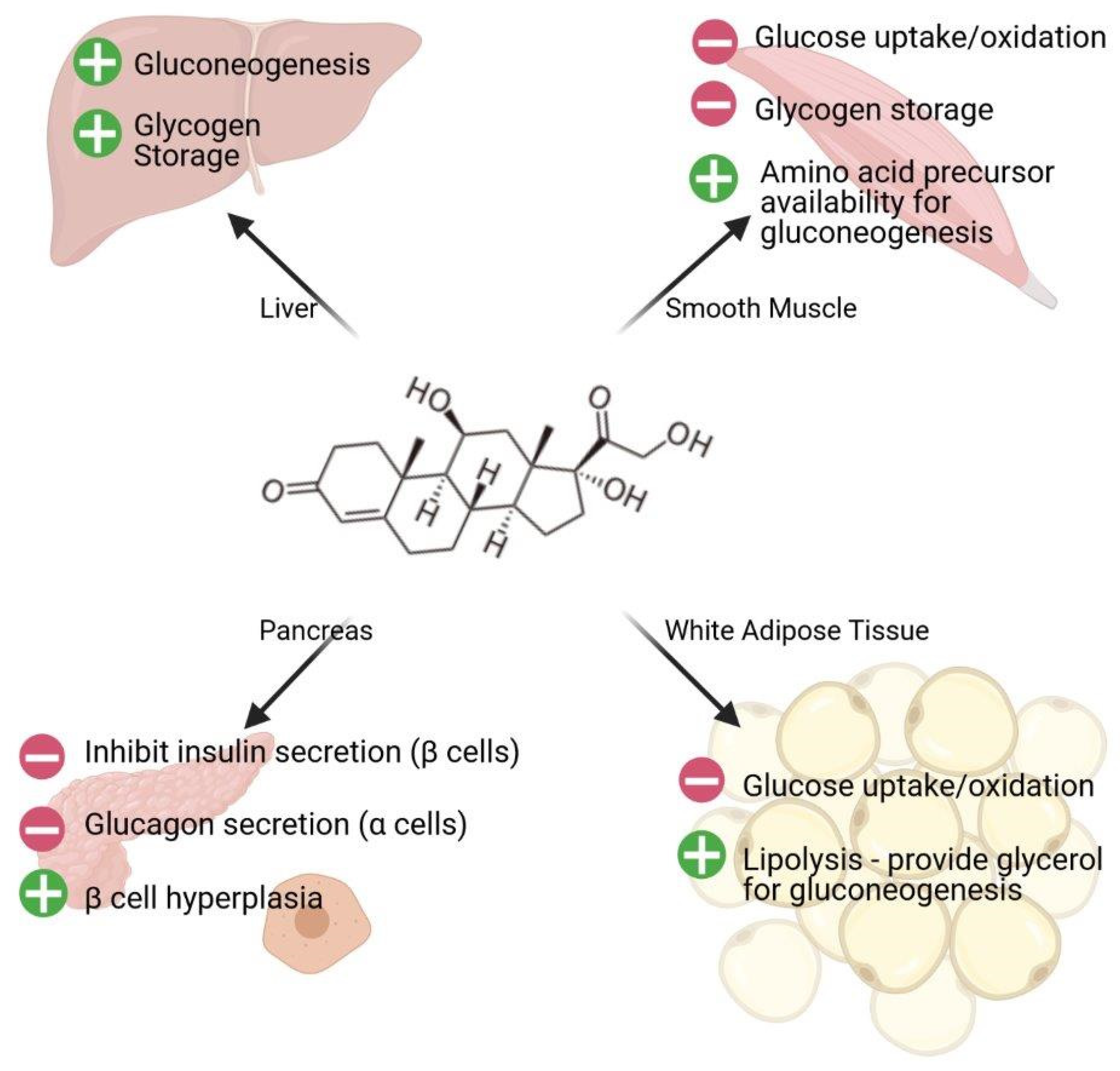
GC promote gluconeogenesis mainly through activation of the transcription of genes encoding enzymes in the gluconeogenic pathway.

. Cortisol stimulates gluconeogenesis the process that synthesizes glucose from oxaloacetate to increase blood. Release chemicals into ducts. It helps the homeostasis of water and electrolytes small substances that contain ions.
Other important functions of cortisol in the body include the following. The complex enters the nucleus and Binds through the zinc fingers to the glucocorticoid response element GRE associated with the PEPCK gene which Increases gene expression. Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the production of glucose from glucogenic amino acids lactate or glycerol 3- phosphate found in triglycerides.
Cortisol stimulates gluconeogenesis through which of the following mechanisms. A-Phosphorylating hormone sensitive lipase b-Decreasing levels of fructose 2 6 biphosphate c-Activatingphosphofructokinase-1 d-Increasing levels of PEPCK phosphoenol carboxykinase. Release chemicals into body cavities.
GC convey their signals mainly through an intracellular receptor the glucocorticoid receptor GR. Cortisol is also involved in glycogenolysis the breakdown of glycogen stored in the liver and muscle cells which is necessary as it activates glycogen phosphorylase an enzyme needed to complete the whole process. Reduced F26-BP synthesis simultaneously removes the stimulation of phosphofructokinase-1 while increasing the activity of F16-BP.
3 The rest of the reactions are reversible and common with gluconeogenesis. Cortisol counters insulin by encouraging higher blood sugar and stimulating gluconeogenesis the metabolic pathway that synthesizes glucose from oxaloacetate. Describe how the ratio of insulin to glucagon cortisol and epinephrine regulate the activity of the regulatory enzymes in each pathway glycogenolysis gluconeogenesis beta oxidation glycolysis fatty.
Various signaling pathways governed by insulin converge at the level of transcriptional regulation of the key hepatic gluconeogenic genes PCK1 and G6PC highlighting this as one of the focal mechanisms through which gluconeogenesis is modulated. Reduction of fructose-26-bisphosphatase F26-BP formation. Release chemicals into the brain Hormones are not a major.
Decreasing levels of fructose 26 bisphosphate Response Feedback. This results in an increase in conversion of F16-BP to. Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam.
Cortisol is involved in maintaining the cardiovascular system as well as the kidney functions. When cortisol is elevated it increased gluconeogenesis by increasing phosphoenol-pyruvate carboxykinase PEPCK. Cortisol stimulates the production of RANKL by osteoblasts which stimulates through binding to RANK receptors the activity of osteoclasts cells responsible for calcium resorption from bone and also inhibits the production of osteoprotegerin OPG which acts as a decoy receptor and captures some RANKL before it.
Cortisol acts on the liver muscle adipose tissue and pancreas. Cortisol after binding its steroid receptor intracellularly moves inside the cell nucleus and binds with its zinc finger domain the glucocorticoid response element GRE on DNA. Activating protein kinase A thus allowing the catalytic subunit to diffuse into the nucleus and phosphorylate CREB to initiate gene transcription.
In individuals with compromised insulin signaling such as insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes insulin fails to suppress hepatic. Release chemicals carried by the blood. Glucocorticoids particularly cortisol produces anti-inflammatory reactions and suppress the immune response.
And inhibit cellular uptake and utilization of amino acids. Cortisol diffuses into the hepatocyte where it Binds to its receptor. Cortisol induces PEPCK gene expression by the following sequence.
The mechanism behind this is two-fold. Question 2 Glucagon stimulates gluconeogenesis through which of the following mechanisms. Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenesis lipolysis and proteolysis.
Suppresses the action of the immune system. It increases the level of sugar in the blood through gluconeogenesis the process by which cortisol synthesizes glucose. Stimulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis Inhibition of glucose uptake in peripheral tissues Stimulation of fat and amino acid breakdown helps provide.
The transcription of PC PCK1 FBP1 PFKFB1 G6PC and G6P transporter SLC37A4 are all stimulated by GC Fig. A key metabolic response to stress is the hepatic metabolic capacity stimulation promoting free glucose to coping with stress through hepatic gluconeogenesis as well as inhibition of glycolysis and glucose uptake in peripheral tissues 7. Glucocorticoids induce PEPCK gene expression.
Cortisol stimulates gluconeogenesis the making of new glucose in the liver using amino acids lactate glycerol and propionate. Gluconeogenesis a second source of glucose is stimulated by glucagon via two mechanisms. Cortisol stimulates gluconeogenesis through which of the following mechanisms.
It does this by. Start studying the Chapter 11 flashcards containing study terms like The endocrine system consists of glands that. In the liver high cortisol levels increase gluconeogenesis and decrease glycogen synthesis.
Cortisols primary targets are metabolic but it also influences other pathways including ion transport or even the immune response 2. The blood glucose raising effect of synthetic cortisol prednisone has been known for at least 40 years. In the fasted state cortisol has several mechanisms to increase glucose in the body.
The presence of cortisol triggers the expression of enzymes critical for gluconeogenesis facilitating this increase in glucose production. However until now the non-canonical mechanisms of cortisol mediating increases of lactate are unknown.

Gluconeogenesis Function Control Teachmephysiology

Cortisol Protein Catabolism Gluconeogenesis Vasoconstriction Anti Inflammation Youtube

Cortisol And Glucagon Stimulate Gluconeogenesis Through Enhancer Mechanisms Medical School Studying Neuropsychology Endocrine System

Comments
Post a Comment